The Influence of Density Driven Mixing Mechanisms on Ureolysis Induced Carbonate Precipitation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69631/ipj.v2i1nr59Keywords:
MICP, Microbially induced carbonate precipitation, EICP, Enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation, Permeability, High-speed XCT, TomographyAbstract
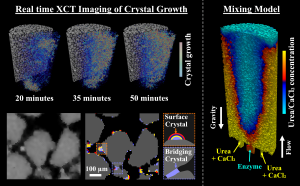
Engineered subsurface barriers with reduced porosity and permeability are critical for safe storage of CO2 and H2, for the prevention of pollutant transport, and for several other subsurface flow challenges. This study investigates enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation (EICP), a promising technique with the potential to achieve uniform precipitation in otherwise inaccessible regions, provided the mechanisms of pore-scale mixing are well understood. High-speed lab x-ray computed tomography and flow modelling were used to study the mechanisms of reagent mixing and precipitation. Our experiments show that initially, crystallization occurs homogeneously across grain surfaces, then localizes in pores with high enzyme concentrations. In these regions, we see crystal growth throughout the 65-minute experiment. Simulation of reagent injection produces a mixing front that matches the distribution of crystals seen in the experiments if we model mixing as a density driven flow. Overall, we see substantial reductions in simulated permeability (11-37%) depending on the efficiency of mixing. Our validated model allows us to predict and propose tailored injection strategies for optimizing mixing, bringing us closer to real-world deployment of EICP for subsurface barriers.
Downloads
References
Baum, D., Weaver, J., Zlotnikov, I., Knötel, D., Tomholt, L., Dean, M. (2019). High-Throughput Segmentation of Tiled Biological Structures using Random Walk Distance Transforms. Integrative and comparative biology, 59, 6. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/icz117
Bernard, D., Guillon, O., Plougonven, E., & Combaret, N. (2011). Constrained sintering of glass films: Microstructure evolution assessed by synchrotron computed tomography. Acta Materialia, vol. 59, 6228-6238 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.06.022
Carmona, J. P. S. F., Oliveira, P. J. V. & Lemos, L. J. L. (2016). Biostabilization of a Sandy Soil Using Enzymatic Calcium Carbonate Precipitation. Procedia Engineering, 143, 1301-1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.144
Chedburn, L., Underhill, J. R., Head, S. & Jamieson, R. (2022). The critical evaluation of carbon dioxide subsurface storage sites: Geological challenges in the depleted fields of Liverpool Bay. AAPG Bulletin, 106, 1753-1789. https://doi.org/10.1306/07062221120
Cheng, L., Shahin, M. A. & Chu, J. (2018). Soil bio-cementation using a new one-phase low-pH injection method. Acta Geotechnica, 14, 615-626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-018-0738-2
Chunxiang, Q., Jianyun, W., Ruixing, W., Liang, C. (2009). Corrosion protection of cement based building materials by surface deposition of CaCO3 by Bacillus pasteurii. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 29 (4), 1273–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2008.10.025
Cui, M.-J., Lai, H.-J., Hoang, T. & Chu, J. (2020). One-phase-low-pH enzyme induced carbonate precipitation (EICP) method for soil improvement. Acta Geotechnica, 16, 481-489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-01043-2
Dobson, K. J., Coban, S. B., McDonald, S. A., Walsh, J. N., Atwood, R. C. & Withers, P. J. (2016). 4-D imaging of sub-second dynamics in pore-scale processes using real-time synchrotron X-ray tomography. Solid Earth, 7, 1059-1073. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-7-1059-2016
Godinho, Ma, Chai, Storm & Burnett. (2019). Mineral Precipitation in Fractures and Nanopores within Shale Imaged Using Time-Lapse X-ray Tomography. Minerals, 9(8), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9080480
Kim, D. H., Mahabadi, N., Jang, J. & Paassen, L. A. (2020). Assessing the Kinetics and Pore‐Scale Characteristics of Biological Calcium Carbonate Precipitation in Porous Media using a Microfluidic Chip Experiment. Water Resources Research, 56. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019WR025420
Konstantinou, C., Wang, Y., & Biscontin, G. (2023). A Systematic Study on the Influence of Grain Characteristics on Hydraulic and Mechanical Performance of MICP-Treated Porous Media. Transport in Porous Media, 147(2), 305-330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-023-01909-5
Krevor, S., De Coninck, H., Gasda, S. E., Ghaleigh, N. S., De Gooyert, V., et al. (2023). Subsurface carbon dioxide and hydrogen storage for a sustainable energy future. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 4, 102-118. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-022-00376-8
Li, X., Tao, J. & van Paassen, L.A. (2024). Reactive transport modeling of microbial-induced calcite precipitation treatment through shallow underwater injection. Computers and Geotechnics, 174, 106601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2024.106601
Lin, Q., Neethling, S. J., Dobson, K. J., Courtois, L. & Lee, P. D. (2015). Quantifying and minimising systematic and random errors in X-ray micro-tomography based volume measurements. Computers & Geosciences, 77, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2014.12.008
Menke, H. P., Reynolds, C. A., Andrew, M. G., Pereira Nunes, J. P., Bijeljic, B. & Blunt, M. J. (2018). 4D multi-scale imaging of reactive flow in carbonates: Assessing the impact of heterogeneity on dissolution regimes using streamlines at multiple length scales. Chemical Geology, 481, 27-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.01.016
Minto, J. M., Hingerl, F. F., Benson, S. M. & Lunn, R. J. (2017). X-ray CT and multiphase flow characterization of a ‘bio-grouted’ sandstone core: The effect of dissolution on seal longevity. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 64, 152-162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2017.07.007
Nemati, M. & G. Voordouw. (2003). Modification of porous media permeability, using calcium carbonate produced enzymatically in situ. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 33, 635-642. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(03)00191-1
Nemati, M., Greene, E. A. & Voordouw, G. (2005). Permeability profile modification using bacterially formed calcium carbonate: comparison with enzymic option. Process Biochemistry, 40, 925-933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.02.019
Otsu, N. (1979). A thresholding selection method from grayscale histogram. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 9(1), 62-66. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076
Peng, S., Di, H., Fan, L., Fan, W., & Qin, L. (2020). Factors Affecting Permeability Reduction of MICP for Fractured Rock. Frontiers in Earth Science, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2020.00217
Putra, H., Yasuhara, H., Kinoshita, N., Neupane, D. & Lu, C. W. (2016). Effect of Magnesium as Substitute Material in Enzyme-Mediated Calcite Precipitation for Soil-Improvement Technique. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 4, 37. http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2016.00037
Putra, H., Yasuhara, H., Kinoshita, N., Erizal & Sudibyo, T. (2018). Improving Shear Strength Parameters of Sandy Soil using Enzyme-Mediated Calcite Precipitation Technique. Civil Engineering Dimension, 20, 91-95. https://doi.org/10.9744/ced.20.2.91-95
Ringrose, P. S. & Meckel, T. A. (2019). Maturing global CO2 storage resources on offshore continental margins to achieve 2DS emissions reductions. Scientific Reports, 9, 17944. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54363-z
Schindelin, J., Arganda-Carreras, I., Frise, E., Kaynig, V., Longair, M., et al. (2012). Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nature Methods, 9, 676-682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2019
Singh, A., Paramkusam, B. R. & Maiti, P. R. (2021). Cyclic degradation and pore pressure dynamics of EICP treated hydrocarbon contaminated sands. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 140, 106369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2020.106369
Studholme, C., Hill, D. L. G., Hawkes, D. J. (1999). An overlap invariant entropy measure of 3D medical image alignment. Pattern Recognition, Volume 32, Issue 1, 71-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(98)00091-0
Wang, H., Sun, X., Miao, L., Cao, Z., Fan, G. & Wu, L. (2022). Induced CaCO3 mineral formation based on enzymatical calcification for bioremediation under different pressure conditions. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 216, 110787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110787
Weinhardt, F., Class, H., Dastjerdi, S. V., Karadimitriou, N., Lee, D., Steeb, H. (2021). Experimental Methods and Imaging for Enzymatically Induced Calcite Precipitation in a Microfluidic Cell. Water Resources Research. 57, 3, e2020WR029361. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020WR029361
Willems, C. J. L., Cheng, C., Watson, S. M., Minto, J., Williams, A., et al. (2021). Permeability and Mineralogy of the Újfalu Formation, Hungary, from Production Tests and Experimental Rock Characterization: Implications for Geothermal Heat Projects. Energies, 14, 4332. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14144332
Yang, Y., Chu, J., Liu, H. & Cheng, L. (2023). Improvement of uniformity of biocemented sand column using CH3COOH-buffered one-phase-low-pH injection method. Acta Geotechnica, 18, 413–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-022-01576-8
Yasuhara, H., Neupane, D., Hayashi, K., and Okamura, M. (2012). Experiments and predictions of physical properties of sand cemented by enzymatically-induced carbonate precipitation. Soils and Foundations, 52, 539–549. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2012.05.011
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Philip J. Salter, James M. Minto, Jay Warnett, Katherine J. Dobson

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Unless otherwise stated above, this is an open access article published by InterPore under either the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Article metadata are available under the CCo license.
How to Cite
Funding data
-
Natural Environment Research Council
Grant numbers NE/T00908X/1 -
UK National Ion Beam Centre
Grant numbers EP/T023198/1













